

Definition of USB Cable
USB or Universal Serial Bus is a well-known industry standard in the tech world known for establishing short-distance digital data communication, connection, and even power supply between peripheral devices and computers. USB was developed for easy connection between peripheral devices like keyboards, mice, printers, scanners, digital cameras and so on without restarting a computer. But since 1997 when computer manufacturers began to use USB ports to replace serial and parallel ports on computer devices, the USB soon had more functions other than just connecting computers to peripheral devices. And now almost all personal computers or laptops have at least 4 ports and numerous devices other than peripheral devices also have USB ports. So,
A USB cable is a cable with different USB connector types for establishing connections, communication and power supply to devices with USB ports. A USB port, on the other hand, is a standard cable connection interface usually used to connect USB devices via a USB cable. The ports can be used to transfer digital data or supply electric power across USB cables. Although there are both wired and wireless versions of the USB standard interface, only the wired version involves USB cable and USB ports.
USB cables can generally be classified based on their speed standard or bandwidth and rate of digital data transmission.

USB 1.0 was the first specification to be released in January 1996 and it allowed a transfer of 1.5Mbit/s at minimum speed and 12Mbit/s at full speed. Later, it was modified and USB 1.1 was released in August 1998 and became the first widely used USB version till it was phased out by USB 2.0.

The USB 3.0 specification, released in 2008, added a Superspeed transfer mode with a signaling rate of 5Gbit/s. USB 3.1 was released with 2 variants: one preserving the Superspeed transfer mode and the second introducing the Superspeed+ transfer mode with a maximum data signaling rate of 10Gbit/s. USB 3.2 preserved both Superspeed and Superspeed+ transfer modes and introduced two new Superspeed+ transfer modes over the USB Type C connector with the signaling rates of 10Gbit/s and 20Gbit/s.

In modern society, USB technology can be found almost everywhere in at least one or two devices that people use every day. However, USB cables have different connections most of which are incompatible with each other because you can't use a different USB cable plug type to connect to another USB connector port.

Type-A USB connectors are currently the most common and easily found plug found at the end of almost every USB cable. They can be used to connect devices such as mice, keyboards, cameras, smartphones and so on to computers. They can also be used to plug into wall chargers or power banks used for charging different gadgets. USB-A cables plug is usually connected to the computer or PC through one port. To avoid damaging the cable or the device you're connecting to, you have to make sure you insert the cable in the right way. A USB-A connector is usually rectangular with a height of 0.65cm and a length of 1.4cm.

USB Type-B cables are not as common to see as Type A, neither are they as versatile as the other USB cables because they are mostly used to connect scanners, routers, printers and some game consoles to computers. The square-shaped USB-B cable has a beveled exterior corner at its top ends.
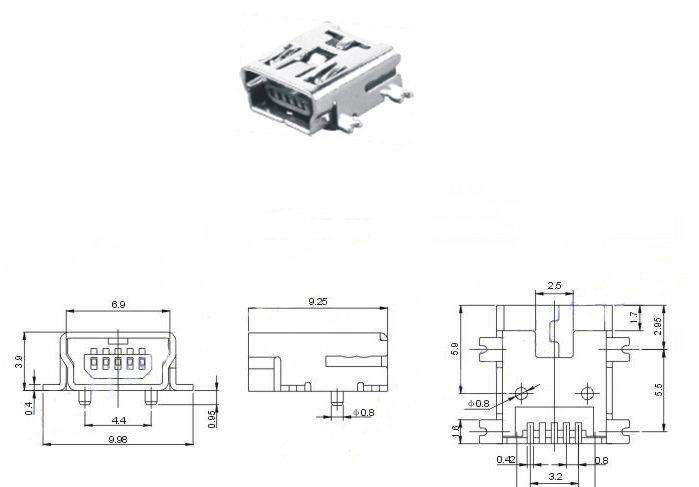
Mini USB connectors have a much more compact design compared to the standard USB-A and USB-B connectors. Compared to its successor (USB-B), the mini USB used to be the smaller USB until it was replaced and phased out by the subsequent Micro USB. Before it was replaced, it was mostly used for connecting mobile devices such as MP3 players and cameras. Mini USB A and B have similar shapes but Mini A sides are straight while Mini B's sides are rounded.
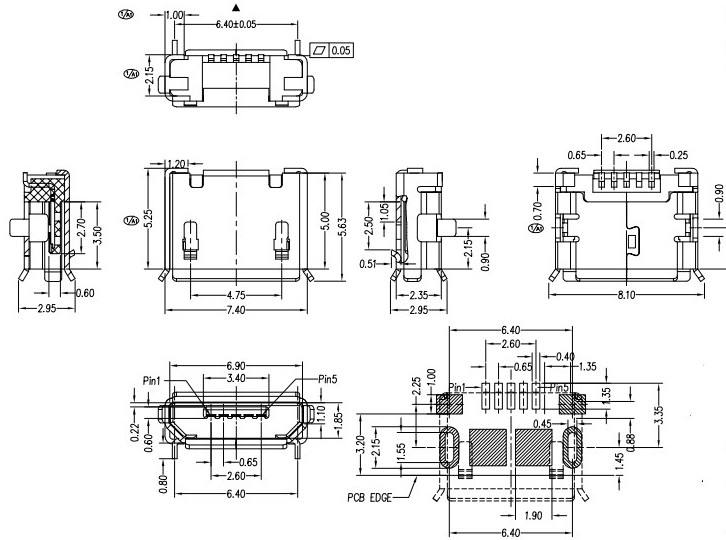
The Micro USB connector was produced before USB Type-C and used to be found on most smartphones, tablets and other devices till it was replaced and gradually phased out by USB-C. Like previous models, micro USB plugs will only go into a plug if it's affixed the right way. If not, it can cause damage to your cable or devices.
The Micro USB is a portable version supporting the USB 2.0 standard. It has a plug life and strength up to 10,000 times stronger than the Mini USB. Although it has a blind plug design, it also supports USB OTG function which allows you to directly transmit data between compatible portable devices, for example, flash drives and memory sticks can be connected directly to mobile devices. The Micro USB also provides for the convenience of emergency charging of your phone with a USB car charger.
USB-C is the latest USB port that can be found on the newer models of smartphones and other mobile devices. It offers a faster digital data transfer rate and a higher power flow than the other previous USB versions. Although some manufacturers are still releasing affordable phones with micro USB ports, USB Type C has become the new standard for smartphones.
Type C USB is 0.84cm long and 0.26cm wide and it offers smaller ports which are 1/3 the size of a standard USB type A plug. As such it supports the thinner, smaller and compact design of many smartphones and mobile devices. It also has the advantage of being reversible and can be plugged in either up or down.
The Type C USB interface with its double-sided interface is usually located at the bottom of smartphones and supports thinner/lighter USB cables. Apart from its ultra-thin appearance, the front and back of USB Type-C ports are the same, meaning that users don't have to worry about the pros and cons of the typical USB port and whatever way they insert the port is correct.
The Micro USB may be narrower than Type-C, however, it is much thicker than type C which is usually light and thin.
The Micro USB has different positive and negative directions design such that inserting the wrong plug can not only affect the plug, it can also damage the mobile device. On the other hand, there is no difference between the negative and positive directions of USB Type C.
USB Type C has a much faster data transfer than Micro USB. It also offers an increased maximum power output and increased charging speed as compared to Micro USB. This is because Micro USB's interface limits the highest voltage output and is thus, limited in charging technology.
Although the USB Type C is more functional in terms of power supply and data transmission, it’s less practical than the Micro USB. This is because most mobile phones in China use the Micro USB interface and finding a Type-C cable is much more difficult than finding a micro USB cable. On the other hand, Micro USB cables are much easier to find.
 The USB 3 was designed to be compatible with the earlier versions of USB cables and ports such as Type A and Type B. The USB 3-A cable is identical to USB Type-A and USB 3-B is identical to USB Type B, however, the USB 3 is colored blue inside. USB 3 also has connector pins that are shaped differently to enable them to withstand more frequent use. The USB Micro also has more pins for transmission of more data.
The USB 3 was designed to be compatible with the earlier versions of USB cables and ports such as Type A and Type B. The USB 3-A cable is identical to USB Type-A and USB 3-B is identical to USB Type B, however, the USB 3 is colored blue inside. USB 3 also has connector pins that are shaped differently to enable them to withstand more frequent use. The USB Micro also has more pins for transmission of more data.
There are many USB cables in use today, some have been phased out, some are currently the most commonly used while others are set to become the new standard for connecting mobile devices and smartphones now and in the future. Of course, there is also the fact that the application scope of the most current USB interface is still somewhat limited. Inevitably, the future of the USB interface and the Smartphone market still has a lot of development space.
Related Products
